常用组件
服务发现 与注册 :eureka、nacos、consul
负载均衡:ribbon、dubbo
服务互相调用:openFeign、dubbo
服务容错:hystrix、sentinel
网关:gateway、zuul
配置统一管理:config-server、nacos、apollo
消息总线:bus
安全组件:security、oauth2.0
服务监控:admin
链路追踪:sleuth+zipkin
Spring Cloud Eureka
CAP原则
在一个分布式系统中具有以下要求:
一致性(consistency):功能相同的节点数据一致
可用性(availability):当一个节点挂掉后,对外的服务依旧可用
分区容错性(partition tolerance):由于网络传输的原因会导致各节点中的数据存在短暂不一致
CAP原则指这三个要素最多只能同时实现两点,不可能三者兼顾
CP:若有个节点挂了,整个服务在一段时间内不能提供服务
AP:故障转移后的服务可能存在数据不一致
zookeeper注重数据的一致性,CP
eureka注重服务的可用性,AP
Eureka配置
可以分为三类:服务端配置、客户端配置、实例配置
服务端配置:
1 2 3 4 eureka: server: eviction-interval-timer-in-ms: 10000 renewal-percent-threshold: 0.85
客户端配置:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 eureka: client: service-url: defaultZone: http://localhost:8761/eureka register-with-eureka: true fetch-registry: true registry-fetch-interval-seconds: 10
实例配置(服务端和客户端都是实例):
1 2 3 4 5 6 eureka: instance: instance-id: ${eureka.instance.hostname}:${spring.application.name}:${server.port} hostname: localhost prefer-ip-address: true lease-renewal-interval-in-seconds: 5
Eureka集群
是去中心化集群,没有主从概念
服务端和客户端都需要加上配置:
1 2 3 4 5 eureka: client: service-url: defaultZone: http://eureka-server-1:8761/eureka,http://eureka-server-2:8762/eureka,http://eureka-server-3:8763/eureka
基础功能及概念
服务的注册
当项目启动(eureka客户端)时,会像eureka-server发送自己的元数据,eureka-server将这些数据保存在内存中,即服务列表
服务的续约
项目启动成功后需要定时向eureka-server报告自己的状态,表示项目还存活
服务的下线(主动下线)
当项目关闭前,发送消息告知eureka-server
服务的剔除(被动下线,主动剔除)
当项目超过指定时间依旧没有向eureka-server续约,eureka-server会认为此项目已经不可用,将它剔除,后面的流量和请求不再到此节点
服务发现
通过服务的应用名称找到服务的具体实例的过程
运行原理
eureka-server对外提供restful风格的服务
通过这些http接口来实现各功能
客户端发送注册请求的类为DiscoveryClient
服务端注册实例的类为InstanceRegistry
服务列表是一个ConcurrentHashMap
服务发现
客户端示例代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 @Autowired private DiscoveryClient discoveryClient; @GetMapping("test") public String test (String serviceId) {if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(instances)) {return "no instance found" ;"{}" , i));return instances.get(0 ).getInstanceId();
Ribbon
主要提供负载均衡算法和服务调用
可以和RestTemplate或者OpenFeign结合使用
eureka-client的依赖中已经包含了ribbon,不需要重复导入依赖
使用RestTemplate
1 2 3 4 5 6 @Bean @LoadBalanced public RestTemplate restTemplate () return new RestTemplate ();
调用
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 @Autowired private RestTemplate restTemplate;@GetMapping("test") public String test (String serviceName) {return restTemplate.getForObject("http://" + serviceName + "/api/a" , String.class);
原理
拦截发送的请求
获取请求中的主机名
使用eureka来做服务发现:loadBalancerInterceptor->blockingLoadBalancerClient.execute()
通过负载均衡算法,获取到一个服务:默认使用轮询的算法(roundRobinLoadBalancer.choose()->processInstanceResponse()->getInstanceResponse())
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 private Response<ServiceInstance> getInstanceResponse (List<ServiceInstance> instances) {if (instances.isEmpty()) {if (log.isWarnEnabled()) {"No servers available for service: " + serviceId);return new EmptyResponse ();if (instances.size() == 1 ) {return new DefaultResponse (instances.get(0 ));int pos = this .position.incrementAndGet() & Integer.MAX_VALUE;ServiceInstance instance = instances.get(pos % instances.size());return new DefaultResponse (instance);
重构请求地址
负载均衡算法
轮询:原子类计数器(CAS操作)+取模运算
随机
权重:对轮询的增强,响应速度越快权重越大,被选到的概率越高
iphash
BestAvailableRule:最优可用,判断最优其实用的是并发连接数,选择并发连接数较小的server发送请求
AvailabilityFilteringRule:可用性过滤规则,先过滤掉不可用的Server实例,再选择并发连接最小的实例
RetryRule:先按轮询策略获取服务,若获取服务失败则在指定的时间内进行重试
ZoneAvoidanceRule:区域内可用性能最优,首先判断一个zone的运行性能是否可用,剔除不可用的区域zone的所有server,然后再利用AvailabilityPredicate过滤并发连接过多的server
相关配置
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 ribbon: eager-load: enabled: false eureka: enabled: true http: client: enabled: false okhttp: enabled: false
OpenFeign
是一个声明式(加注解)的Web服务客户端,通过创建接口加上注解即可
默认集成了ribbon,ribbon又集成了eureka
使用示例
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 @FeignClient(value = "jdap-cloud-eureka-client-a", path = "api") public interface ClientApiFeign {@GetMapping("a") a () ;
启动类加上@EnableFeignClients注解,开启feign的客户端功能
使用:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 @Autowired private ClientApiFeign clientApiFeign;@GetMapping("testFeign") public String testFeign () {return clientApiFeign.a();
原理
本质就是JDK动态代理
项目启动扫描注解,给接口创建代理对象
代理对象执行invoke方法
在invoke方法里面做远程调用
调用参数处理
传参需要确保调用方和提供者的参数列表一致,包括返回值(方法签名一致)
通过URL传参数,GET请求,参数列表使用@PathVariable
若是GET请求,每个基本参数必须加@RequestParam
若是POST请求,而且是对象集合参数,必须加@RequestBody或@RequestParam
不建议单独传递Date类型参数,可以改为:
Hystrix
Hystrix是一个熔断器,也叫断路器,从来保护微服务不雪崩 的方法
熔断器能够阻止分布式系统中出现联动故障
Hystrix通过隔离服务的访问点阻止联动故障,并提供了故障的解决方案,从而提高了整个分布式系统的弹性
一般和Feign、Ribbon一起使用
使用方式
引入依赖:
1 2 3 4 <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.cloud</groupId > <artifactId > spring-cloud-starter-netflix-hystrix</artifactId > </dependency >
启动类加上注解@EnableHystrix
编写接口调用失败后的备选方案
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 @Component public class ClientApiFeignHystrix implements ClientApiFeign {@Override public String a () {return "backup" ;
设置接口fallback属性来设置备选方案
1 2 3 4 5 6 @FeignClient(value = "jdap-cloud-eureka-client-a", path = "api", fallback = ClientApiFeignHystrix.class) public interface ClientApiFeign {@GetMapping("a") a () ;
feign的配置中开启
1 2 3 feign: hystrix: enabled: true
原理
熔断器类似于一个拦截器 ,在执行请求之前先进行判断
默认情况下熔断器是关闭的
当一个时间窗口内访问失败次数超过了一个阈值,熔断器进入关闭状态
一段时候后熔断器变为半开状态,半开的意思就是允许少许流量去尝试远程调用,若调用成功会将熔断器设置关闭状态
Sleuth
链路追踪,追踪微服务的调用路径
一般不建议链路调用超过3次
Sleuth+Zipkin实现分布式链路调用的监控,Zipkin是一个可视化的监控控制台
Spring Boot Admin
用于服务监控,单独起一个服务,被监控的服务需要引入指标监控(actuator)依赖,并在配置文件中暴露监控指标
1 2 3 4 <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId > </dependency >
1 2 3 4 5 management: endpoints: web: exposure: include: '*'
Spring Cloud Gateway
网关是微服务最边缘的服务,直接暴露给用户,用来做用户和微服务的桥梁
路由转发,安全控制,负载均衡
Spring Cloud Gateway基于WebFlux框架实现
网关的核心就是路由转发 和执行过滤器链
三大核心概念:路由,断言,过滤
路由(Route)
路由信息的组成:由一个ID、一个目的URL、一组断言工厂、一组过滤器组成
若路由断言为真,说明请求URL和配置路由匹配
可以和eureka结合做动态路由
断言(Predicate)
断言就是个返回bool的表达式
过滤(Filter)
一个标准的WebFilter
Spring Cloud Gateway中过滤器分为两种,分别是Gateway Filter和Global Filter
一个是针对某一个路由的过滤器,如对某个接口做限流
一个针对全局的过滤器,如IP黑名单
网关集群
使用nginx实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 upstream www.mygateway.com {
配置文件路由
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 spring: application: name: gateway-server cloud: gateway: routes: - id: module1-service uri: http://localhost:11001 predicates: - Path=/module1/**
配置类路由
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 @Configuration public class RouteConfig {@Bean public RouteLocator customRouteLocator (RouteLocatorBuilder builder) {return builder.routes()"module2_service" , r -> r.path("/module2/**" )"http://localhost:11002" ))
动态路由
结合eureka实现
引入eureka-client依赖
网关配置文件中开启动态路由
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 spring: application: name: gateway-server cloud: gateway: discovery: locator: enabled: true lower-case-service-id: true routes: - id: module1-service uri: lb://module1-service predicates: - Path=/module1/**
使用ip:port/服务名称小写/调用路径 的形式访问
断言工厂
Spring Cloud Gateway 官方文档
Spring Cloud Gateway 中文文档
可以用逻辑 and 语句组合多个路由谓词工厂
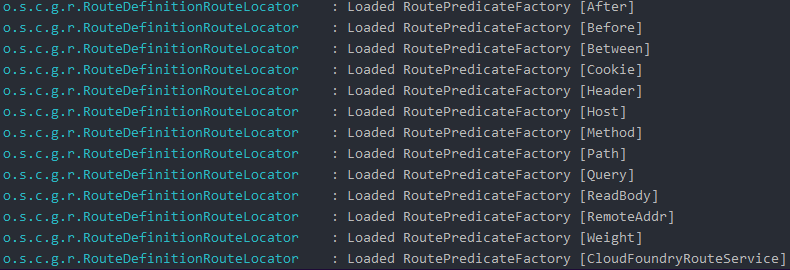
After:匹配发生在指定日期时间之后的请求
Before:匹配发生在指定时间之前的请求
Between:匹配发生在两个时间之前的请求
Cookie:匹配具有给定名称且其值符合正则表达式的cookie
Header:与具有给定名称且其值与正则表达式相匹配的 header 匹配
Host:匹配符合该pattern的Host header
Method:匹配请求方式
Path:对路径进行匹配
Query:请求参数路由匹配
RemoteAddr:若请求的远程地址符合条件则匹配
Weight
XForwarded Remote Addr
过滤器工厂
gatewayfilter-factories
global-filters
自定义全局过滤器
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 @Component public class MyGlobalFilter implements GlobalFilter , Ordered {@Override public Mono<Void> filter (ServerWebExchange exchange, GatewayFilterChain chain) {return chain.filter(exchange);@Override public int getOrder () {return 0 ;
IP黑名单过滤器
原理就在在缓存中保存IP黑名单,判断请求来源IP是否在黑名单中
Token验证过滤器
原理就是登录后创建一个凭证放到redis中,再返回给前端,之后前端的请求需要携带此凭证,过滤器从Header或Cookie中获取凭证,查询redis判断是否存在,存在则说明是已登录状态,可以放行
限流过滤器
IP限流:控制同一个IP在一段时间内的访问次数,避免频繁访问
请求量限流:在一段时间内,全部请求次数达到阈值,就直接拒绝后面来的请求
常见的限流模型有:漏斗算法,令牌桶算法,滑动窗口算法,计数器算法
令牌桶算法的原理:令牌以一定速度不断生成,放入桶中,当达到桶的上限时不再生成
结合Redis实现请求量限流,且已内置了RequestRateLimiterGatewayFilterFactory
添加依赖
1 2 3 4 <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-data-redis-reactive</artifactId > </dependency >
实现KeyResolver
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 @Configuration public class RequestLimitConfig {@Bean(name = "ipKeyResolver") public KeyResolver ipKeyResolver () {return exchange -> Mono.just(Objects.requireNonNull(@Bean(name = "apiKeyResolver") public KeyResolver apiKeyResolver () {return exchange -> Mono.just(
路由中配置过滤器
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 spring: application: name: gateway-server cloud: gateway: discovery: locator: enabled: true lower-case-service-id: true routes: - id: module1-service uri: lb://module1-service predicates: - Path=/module1/** filters: - name: RequestRateLimiter args: key-resolver: redis-rate-limiter.replenishRate: 1 redis-rate-limiter.burstCapacity: 3
跨域配置
在类上方法上加@CrossOrigin注解可以使对应的类中的所有方法和方法允许跨域请求
本质就是过滤器
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 @Configuration public class CorsConfig {@Bean public CorsWebFilter corsWebFilter () {CorsConfiguration config = new CorsConfiguration ();"*" );"*" );"*" );UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource source = new UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource (new PathPatternParser ());"/**" , config);return new CorsWebFilter (source);
常见问题
网关的用途
跨域,路由(动态路由,负载均衡),ip黑名单,Token验证,对请求进行过滤,熔断,限流
Gateway与zuul的异同
相同点:
不同点:
Gateway是Spring Cloud官方的组件,zuul是netflix的产品
Gateway在spring的支持下,内部实现了限流、负载均衡等,扩展性也更强,但同时也限制了仅适合于Spring Cloud下;zuul可扩展至其他微服务框架中,其内部没有实现限流、负载均衡等
Gateway很好的支持异步(响应式编程模式是异步的,基于netty),而zuul1.0仅支持同步,zuul2.0之后也支持异步
Spring Cloud Alibaba
Spring Cloud Alibaba致力于提供微服务开发的一站式解决方案,包含开发分布式应用微服务的必需组件
组件
Nacos :服务治理,注册中心和配置文件中心Sentinel:服务保护,类似于熔断器
Dubbo:远程调用
Seata:分布式事务
消息驱动:RocketMQ
Nacos
Nacos注册中心
引入依赖
1 2 3 4 <dependency > <groupId > com.alibaba.cloud</groupId > <artifactId > spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-discovery</artifactId > </dependency >
修改配置
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 spring: application: name: client2-service cloud: nacos: server-addr: localhost:8848 username: nacos password: nacos discovery: namespace: 65571c08-df2c-4d16-80e4-65e92afa79f5 group: A_GROUP
不同命名空间内的服务无法互相发现,不同分组的服务也无法互相发现
即只有同命名空间且同分组内的服务可以互相发现
服务发现使用
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 @Autowired private DiscoveryClient discoveryClient;@GetMapping("test") public String test () {"client2-service" );if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(instances)) {return "instance not found" ;return instances.get(0 ).toString();
启动类上加上@EnableDiscoveryClient注解
Nacos注册中心与eureka区别
Nacos默认有账号密码访问,eureka对访问默认没有控制
Nacos有命名空间,隔离
整合Gateway
引入依赖
1 2 3 4 <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.cloud</groupId > <artifactId > spring-cloud-starter-gateway</artifactId > </dependency >
修改配置文件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 spring: application: name: gateway-server-service cloud: nacos: server-addr: localhost:8848 username: nacos password: nacos discovery: namespace: 65571c08-df2c-4d16-80e4-65e92afa79f5 group: A_GROUP gateway: discovery: locator: enabled: true lower-case-service-id: true
启动类上加上@EnableDiscoveryClient注解
使用ip:port/服务名称小写/调用路径 的形式访问
配置文件中心
引入依赖
1 2 3 4 <dependency > <groupId > com.alibaba.cloud</groupId > <artifactId > spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-config</artifactId > </dependency >
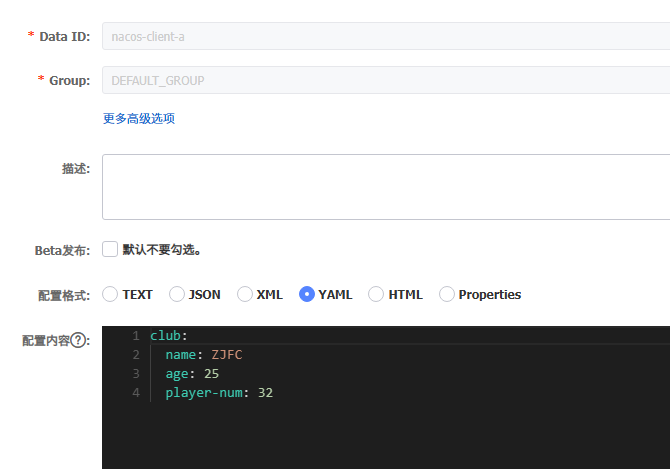
新增bootstrap.yml配置文件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 spring: cloud: nacos: config: server-addr: localhost:8848 username: nacos password: nacos name: nacos-client-a file-extension: yml namespace: 65571c08-df2c-4d16-80e4-65e92afa79f5 group: DEFAULT_GROUP
编写配置类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 @RefreshScope @Configuration @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "club") @Data public class ClubConfig {private String name;private Integer age;private Integer playerNum;
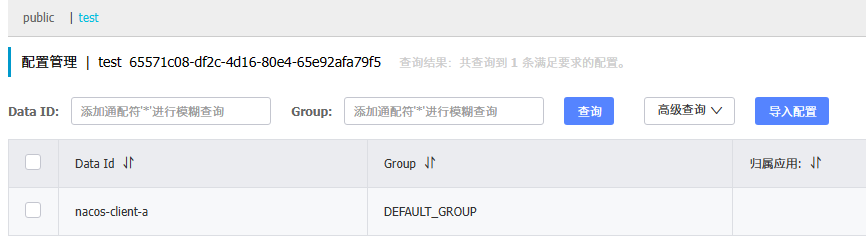
在nacos配置管理指定命名空间和分组中新建一个同名的配置
更详细地配置可以参考Nacos Spring Cloud 快速开始